What is an ATP BlockDAG Server? A Complete Guide

Blockchain technology has transformed digital transactions, but it faces major scalability and efficiency challenges. To overcome these, BlockDAG (Block Directed Acyclic Graph) technology has emerged as a superior alternative.
At the heart of this innovation lies the ATP BlockDAG Server, a powerful system designed to support decentralized networks with high efficiency, fast transaction speeds, and robust security.
This guide explores everything about ATP BlockDAG Servers, including their functionality, benefits, use cases, and future potential.
Understanding ATP BlockDAG Servers

What is an ATP BlockDAG Server?
An ATP BlockDAG Server is a specialized server designed to handle transactions and data processing within a BlockDAG-based network. Unlike traditional blockchain servers, which process transactions in a sequential manner, BlockDAG servers work in parallel, allowing multiple transactions and blocks to be confirmed simultaneously.
Key Features of an ATP BlockDAG Server
- Parallel Transaction Processing: Handles multiple transactions and blocks at the same time.
- Improved Security: Uses cryptographic verification to prevent double-spending and attacks.
- High Scalability: Supports large-scale decentralized applications (dApps) without congestion.
- Energy-Efficient Mechanism: Reduces the computational workload compared to traditional blockchains.
BlockDAG vs. Blockchain: What’s the Difference?
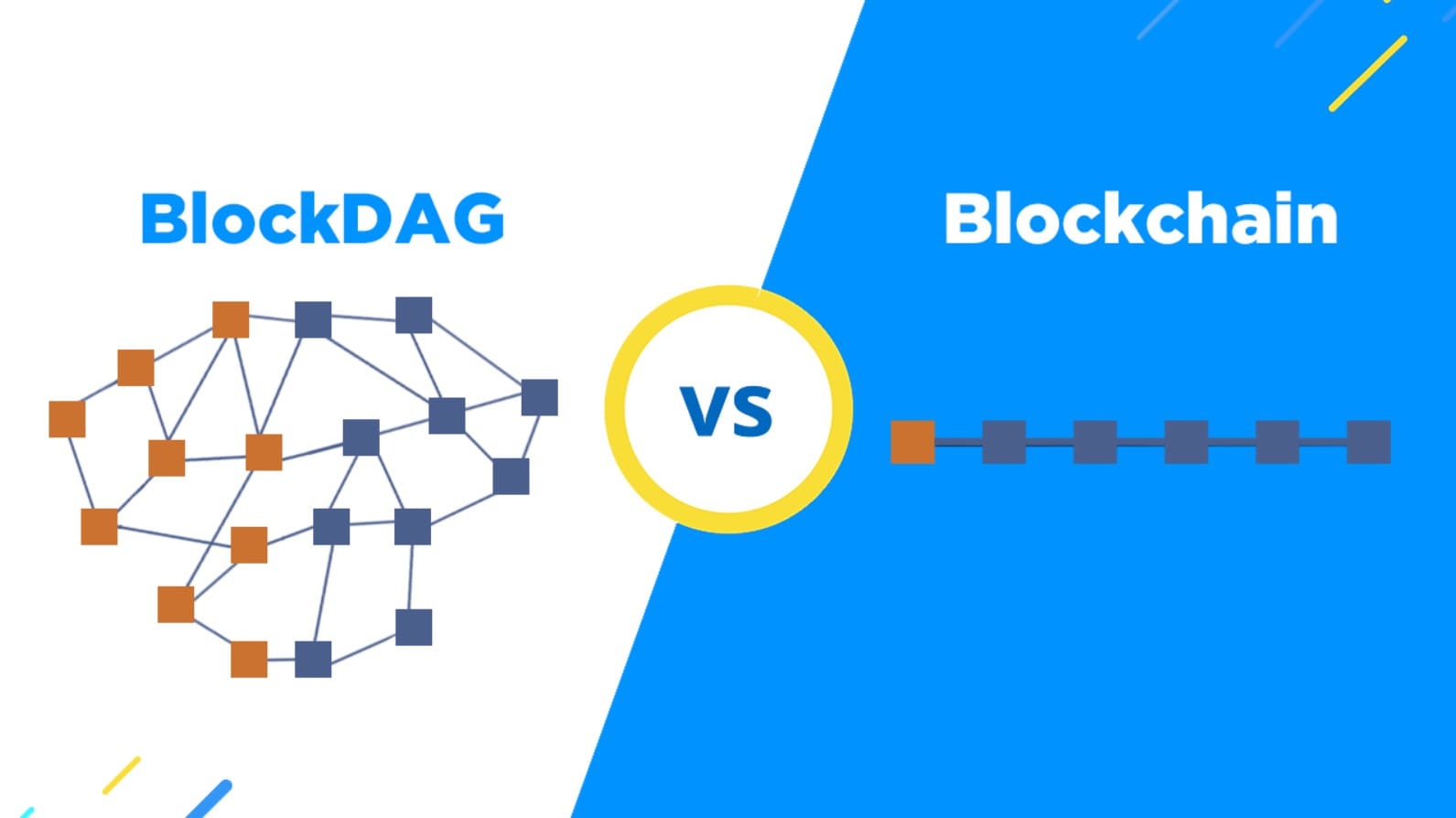
Fundamental Differences Between BlockDAG and Blockchain
| Feature | Blockchain | BlockDAG |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Linear chain of blocks | Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) |
| Scalability | Limited due to single block creation | High due to parallel block creation |
| Transaction Speed | Slower due to sequential processing | Faster due to parallel processing |
| Security | Susceptible to bottlenecks & attacks | Highly secure with multiple verification pathways |
How Does BlockDAG Improve Blockchain Performance?
- Supports Multiple Blocks at Once: Unlike traditional blockchains, where only one block is added at a time, BlockDAG allows multiple blocks to be added simultaneously.
- Minimizes Transaction Delays: BlockDAG eliminates network congestion by processing transactions in parallel.
- Decentralization at Its Core: Due to multiple block pathways, there is no single point of failure, improving system security.
Core Components of an ATP BlockDAG Server
To function effectively, an ATP BlockDAG Server is equipped with several essential components:
1. Node Infrastructure
A decentralized network of nodes powers the ATP BlockDAG Server, ensuring:
- Efficient transaction validation across multiple paths.
- Data synchronization between different nodes.
- Consensus enforcement to maintain network integrity.
2. Consensus Mechanism
ATP BlockDAG Servers use next-generation consensus mechanisms, including:
- Proof-of-Stake (PoS): Reduces energy consumption while increasing transaction speeds.
- Proof-of-Activity (PoA): A hybrid approach that combines mining with active participation.
- DAG-based Proofs: Uses directed acyclic graphs to validate transactions.
3. Transaction Verification Module
This component ensures:
- No double-spending occurs.
- Transactions remain cryptographically secure with multiple verification layers.
- The correct DAG structure is maintained for efficiency.
4. Smart Contract Execution Layer
This layer enables dApp development and automated transactions, making BlockDAG-based applications faster and more reliable than traditional blockchain solutions.
How Does an ATP BlockDAG Server Work?
Step 1: Transaction Submission
Users initiate transactions, which are broadcast across the network.
Step 2: Parallel Processing of Transactions
- Instead of adding a single block at a time (as in blockchain), BlockDAG allows multiple blocks to be created simultaneously.
- This results in higher transaction throughput and reduced confirmation time.
Step 3: Consensus Mechanism Validation
Nodes verify transactions through PoS, PoA, or another consensus method to maintain network security and integrity.
Step 4: Block Addition in the DAG Structure
Validated transactions are added in parallel to the DAG network, ensuring a continuous data flow.
Step 5: Final Confirmation & Security Checks
The network performs final cryptographic verifications, ensuring the transactions follow the DAG structure without conflicts.
Advantages of ATP BlockDAG Servers
1. Enhanced Scalability
- Can process thousands of transactions per second (TPS).
- Supports large-scale decentralized applications without congestion.
2. Faster Transaction Speeds
- Transactions confirm almost instantly due to parallel processing.
- No network delays, even under high transaction volume.
3. Stronger Security
- More resistant to 51% attacks compared to blockchain networks.
- Cryptographic verification prevents fraudulent transactions.
4. Energy-Efficient Operations
- Uses less computational power, making it a sustainable alternative to blockchain.
- Works with eco-friendly consensus models like PoS.
Use Cases of ATP BlockDAG Servers
ATP BlockDAG Servers are transforming industries by offering scalable, secure, and decentralized solutions.
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
- Facilitates secure, high-speed transactions for decentralized lending and trading platforms.
- Eliminates middlemen, reducing transaction fees.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Enables real-time tracking of goods and assets.
- Increases transparency in transactions.
3. Gaming Industry
- Supports secure in-game asset transactions using smart contracts.
- Reduces latency for online multiplayer gaming environments.
4. Internet of Things (IoT)
- Enables secure device-to-device communication in IoT ecosystems.
- Scales efficiently to handle billions of connected devices.
Challenges of ATP BlockDAG Servers
1. Complexity in Implementation
- Requires expert-level technical knowledge to set up.
- Needs highly optimized infrastructure for full-scale adoption.
2. Consensus Mechanism Optimization
- Finding a balance between security and transaction speed remains a challenge.
- Some BlockDAG implementations require customized consensus protocols.
3. Adoption and Compatibility
- Developers need to adapt to new BlockDAG programming models.
- Existing blockchain applications may require significant modifications.
Future of ATP BlockDAG Servers
With continued technological advancements, ATP BlockDAG Servers are expected to reshape decentralized computing.
Key Developments to Watch
- Integration with AI & machine learning to automate network optimization.
- Cross-chain interoperability for seamless interaction between BlockDAG and blockchain networks.
- Decentralized governance improvements for a more democratic network ecosystem.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is an ATP BlockDAG Server different from a blockchain server?
ATP BlockDAG processes multiple blocks in parallel, whereas blockchain follows a sequential structure.
Can ATP BlockDAG Servers be used for smart contracts?
Yes! They fully support decentralized applications and automated contracts.
Are ATP BlockDAG Servers more energy-efficient than traditional blockchain?
Absolutely! They consume less energy due to advanced consensus mechanisms.
Conclusion
ATP BlockDAG Servers are the future of decentralized networks, offering unmatched scalability, speed, and security. As adoption grows, they will become the backbone of next-generation blockchain ecosystems.





